Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an important enzyme found in the liver, bones, kidneys, and digestive system. While normal levels are essential for various bodily functions, high alkaline phosphatase levels may indicate underlying health issues such as liver disease, bone disorders, or vitamin deficiencies. If your ALP levels are elevated, dietary adjustments can help manage and reduce them. So, what foods to avoid if alkaline phosphatase is high? This article explores the key dietary culprits, alternative food choices, and expert recommendations to help maintain optimal enzyme levels.
Understanding High Alkaline Phosphatase Levels
High ALP levels can result from various factors, including liver dysfunction, gallbladder disease, bone disorders (such as osteoporosis), or nutritional imbalances. It is often detected through routine blood tests and requires medical evaluation to identify the root cause.
Diet plays a crucial role in ALP regulation. Consuming the wrong foods may worsen the condition, while a balanced diet can help stabilize enzyme levels and improve overall health.
What Foods to Avoid if Alkaline Phosphatase is High?
1. High-Fat Processed Foods
- Fast food, fried items, and processed snacks increase liver stress, leading to elevated ALP levels.
- Studies suggest that excessive trans fats and saturated fats worsen liver conditions, making it harder for the body to regulate enzyme production.
2. Red and Processed Meats
- Beef, pork, and processed meats (sausages, hot dogs, and bacon) are high in saturated fats, which contribute to liver inflammation.
- Research indicates that high meat consumption correlates with liver enzyme abnormalities, including elevated ALP.
3. Dairy Products with High Saturated Fats
- Whole milk, cheese, butter, and cream may exacerbate liver-related ALP elevation.
- Instead, opt for plant-based dairy alternatives such as almond or oat milk.
4. Refined Sugars and Carbohydrates
- Sugary drinks, pastries, white bread, and candies lead to insulin resistance and liver stress.
- High sugar intake has been linked to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition associated with increased ALP levels.
5. Alcohol and Sugary Beverages
- Alcohol affects liver function, increasing inflammation and contributing to high ALP.
- Soft drinks and fruit juices with added sugars overload the liver, leading to further enzyme imbalance.
6. Excess Phosphorus-Rich Foods
- Organ meats, sodas, processed foods, and dairy products contain high phosphorus levels, which can negatively impact bone and liver health.
- An imbalance in phosphorus may trigger excessive ALP production, affecting bone metabolism.
7. Salt and High-Sodium Foods
- Packaged soups, chips, processed meats, and restaurant foods contain high sodium, leading to liver stress and hypertension.
- A low-sodium diet has been shown to improve liver function and lower ALP levels.
Healthy Alternatives to Support ALP Regulation
Instead of focusing solely on what foods to avoid if alkaline phosphatase is high, it’s equally important to consider healthy alternatives that support liver and bone health.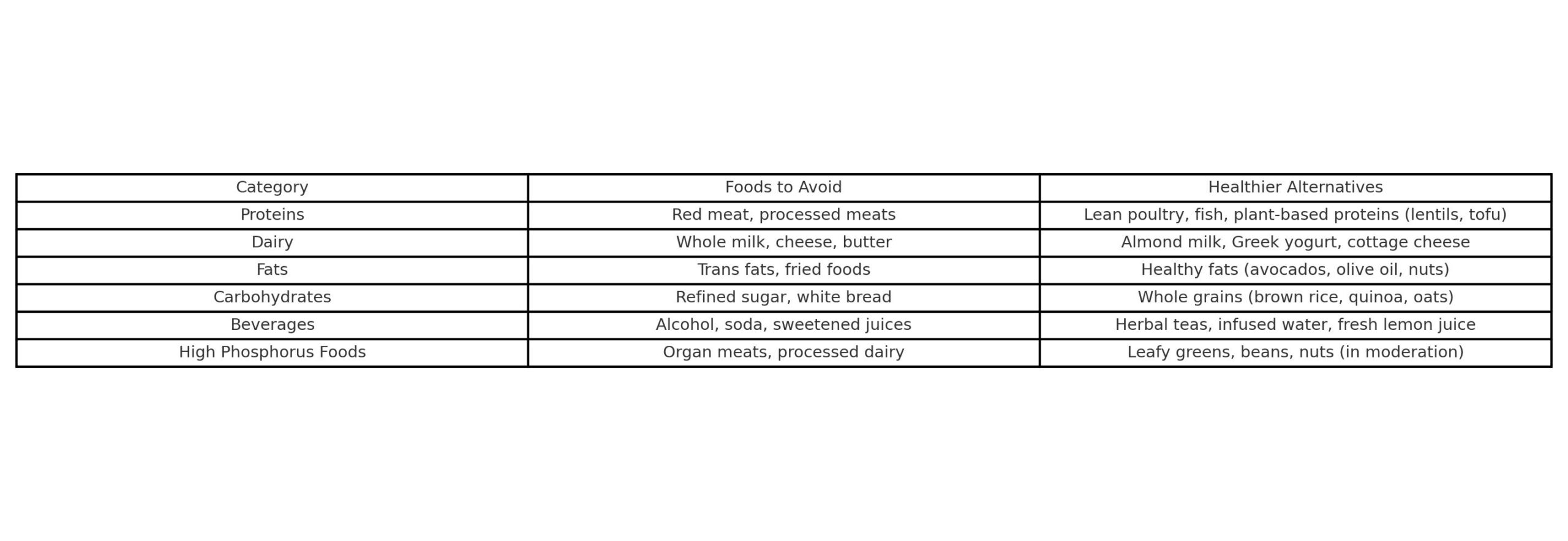 This table provides a quick overview of dietary adjustments to help manage high ALP levels effectively.
This table provides a quick overview of dietary adjustments to help manage high ALP levels effectively.
Tips for Managing High Alkaline Phosphatase Naturally
- Increase Vitamin D Intake
- Low vitamin D levels correlate with high ALP. Sun exposure, fatty fish, and fortified foods help maintain balance.
- Consume Liver-Supporting Foods
- Leafy greens, beets, garlic, and turmeric promote liver detoxification.
- Hydrate Adequately
- Water aids in flushing out toxins and improving overall enzyme regulation.
- Exercise Regularly
- Physical activity supports bone health and enhances liver function, helping stabilize ALP levels.
- Monitor Medications
- Some drugs, like steroids and anti-epileptics, impact ALP levels. Consult a doctor before making changes.
FAQs on Alkaline Phosphatase and Diet
1. What is the main cause of high alkaline phosphatase?
High ALP is often caused by liver disease, bone disorders, gallbladder issues, or vitamin D deficiency.
2. Can diet alone lower alkaline phosphatase levels?
While diet plays a crucial role, managing ALP levels also requires lifestyle changes, medical treatment, and regular monitoring.
3. Are eggs bad for high alkaline phosphatase?
Eggs are generally safe but should be consumed in moderation. Opt for boiled or poached eggs instead of fried versions.
4. Does high ALP mean liver damage?
Not necessarily. It can indicate various conditions, including bone growth, pregnancy, or liver disease. A doctor can help determine the cause.
5. Can exercise help lower ALP?
Yes, regular physical activity improves bone density, liver health, and enzyme balance.
6. What should I drink if my ALP is high?
Stick to water, herbal teas, and antioxidant-rich beverages like green tea or lemon water.
Conclusion
If you’re wondering what foods to avoid if alkaline phosphatase is high, the key is to eliminate processed, high-fat, and phosphorus-rich foods while adopting a nutrient-dense diet. Choosing whole foods, staying hydrated, and maintaining an active lifestyle can significantly help regulate ALP levels. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and create a personalized plan for long-term health.
By making the right dietary choices today, you can take control of your health and prevent complications associated with high alkaline phosphatase levels.